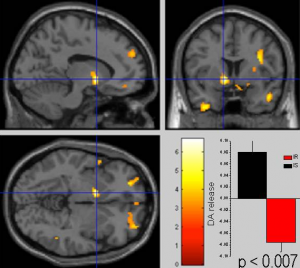
Statistical parameter mapping that compared the difference of [C-11] raclopride scan after oral ingestion of glucose and after oral sucralose (artificial sweetener) drinks between insulin resistance subjects and control subjects.

Statistical parameter mapping that compared the difference of [C-11] raclopride scan after oral ingestion of glucose and after oral sucralose (artificial sweetener) drinks between insulin resistance subjects and control subjects.
Obesity is an epidemic among Americans — an estimated one-third of us are obese, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention — and consequently a major drag on the U.S. health care system. It’s a major root cause of diabetes and the American Diabetes Association estimates that 26 million Americans are living with diabetes and another 79 million are thought to be pre-diabetic, including those with insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance figured in a major study in news released at the 2013 annual meeting of the Society of Nuclear
Using positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of the brain, researchers have identified a spot that gives the wrong signals when simple sugars are introduced to people with insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. For the insulin-resistant, a sugar drink resulted in a below normal release of the chemical dopamine in a major pleasure center of the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps control the brain’s reward and pleasure centers. Dopamine also helps regulate movement and emotional responses, and it enables us not only to see rewards, but to take action to move toward them.
So without that feeling of reward or satisfaction from eating or drinking, we may tend to overeat or over-drink to compensate. This chemical response may be indicative of a deficit reward system, which could potentially be setting the stage for insulin resistance. This research could radically improve medicine’s understanding of how food-reward signaling contributes to obesity. “A better understanding of the cerebral mechanisms underlying abnormal eating behaviors with insulin resistance would help in the development of interventions to counteract the deterioration caused by overeating and subsequent obesity,” said a statement by lead author Dr. Gene-Jack Wang, a professor of radiology at Stony Brook University on Long Island, N.Y.
“We suggest that insulin resistance and its association with less dopamine release in a central brain reward region might promote overeating to compensate for this deficit,” Wand said.
The study involved 19 participants — 11 healthy controls and eight insulin-resistant subjects — who consumed a glucose drink and, on another day, an artificially-sweetened drink. Using PET imaging with an isotope that binds to dopamine receptors, researchers mapped lit-up areas of the brain. Those who were insulin resistant and had disorderly eating patterns were found to have a “remarkably” lower dopamine release.
Researchers believe this study could help develop interventions such as medication or lifestyle modification for early-stage insulin-resistant subjects to counteract the deterioration that leads to obesity and possibly diabetes.
_____________________________
Best quote of SNMMI 2013: Dr. Sang Moo Lim, director of the department of nuclear medicine at the Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences in Seoul, Korea, introducing a study of how imaging can predict the efficacy of chemotherapy for breast cancer:
“In North Korea, they have nuclear weapons. In South Korea, we have strong nuclear medicine.”