Anyone who has a friend or loved one who is undergoing treatment for cancer has probably heard them say at some point, “Sorry, that’s my chemo brain.” It is meant to convey the patient’s confusion or loss of memory relating to chemotherapy.
Anyone who has a friend or loved one who is undergoing treatment for cancer has probably heard them say at some point, “Sorry, that’s my chemo brain.” It is meant to convey the patient’s confusion or loss of memory relating to chemotherapy.
While the complaint may be heard frequently, the cause of the chemo brain phenomenon has been difficult to pinpoint. But using positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography, researchers were able to detect physiological evidence of chemo brain. The study was presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) in Chicago.
Chemotherapy can induce changes in the brain that may affect concentration and memory. “The chemo brain phenomenon is described as ‘mental fog’ and ‘loss of coping skills’ by patients who receive chemotherapy,” said Dr. Rachel Lagos, diagnostic radiology resident at the West Virginia University School of Medicine in Morgantown, W.V. “Because this is such a common patient complaint, healthcare providers have generically referred to its occurrence as ‘chemo brain’ for more than two decades.”
But how do you prove it? Couldn’t it be a side effect associated with the general malaise of cancer treatment? Prior studies using MRIs found some small changes in brain volume after chemotherapy, but no definitive link has been established. Dr. Lagos and fellow researchers looked at brain function, not brain appearance, for evidence. By using PET/CT, they were able to assess changes to the brain’s metabolism after chemotherapy. The changes were surprisingly obvious, said Dr. Lagos. Chemo brain is not a feeling and not depression, she asserted.
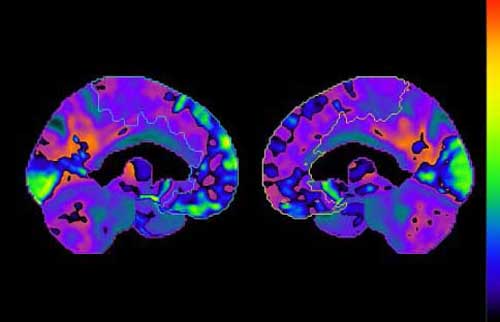
Figure 1. If this map of the brain is divided down the middle and turned towards the sliced sides, the bright yellow and lime green hues in the left superior medial frontal gyrus sharply contrast the cool blue hues in the same region on the right side. The brain uses glucose as its energy supply. The bright colors represent large decreases in glucose usage by the brain.
Researchers analyzed PET/CT brain imaging results from 128 patients who had undergone chemotherapy for breast cancer. Special software enabled them to discern differences in brain metabolism before and after treatment. The scan results demonstrated statistically significant decreases in regional brain metabolism that were closely associated with classic chemo brain symptoms.
“The study shows that there are specific areas of the brain that use less energy following chemotherapy,” said Dr. Lagos. “These brain areas are the ones known to be responsible for planning and prioritizing.” She believes that PET/CT could be used to facilitate clinical diagnosis and allow for earlier intervention and better treatment for patients experiencing this condition. Dr. Lagos also said she hoped that the study would remove any stigma attached to chemo brain.
“Our patients joke about chemo brain affecting their lives,” she said. “As physicians we are struggling to diagnose and treat this side effect to life-saving chemotherapy.”