Technology is always evolving in all sectors, and medicine is no different. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, augmented reality (AR) is being used more often in medical education, radiology, and surgery. Global healthcare companies spent around $600 million on augmeted reality in 2018, but that figure is projected to increase to over $4.2 billion by 2026. This means the market size in this field is growing over 27% a year. Augmented reality applications have increased during the last ten years, mainly in spine surgery and neuronavigation.
Moreover, studies show that AR is slowly becoming a strategic component of neurosurgical training courses. Click here to read more about the latest neurological surgery methods.
Advanced Medical Imaging
There is no doubt that advanced medical imaging has taken the radiology community by storm. Artificial intelligence, augmented reality, three-dimensional printing, cinematic rendering, and digital twin technology have all impacted healthcare.
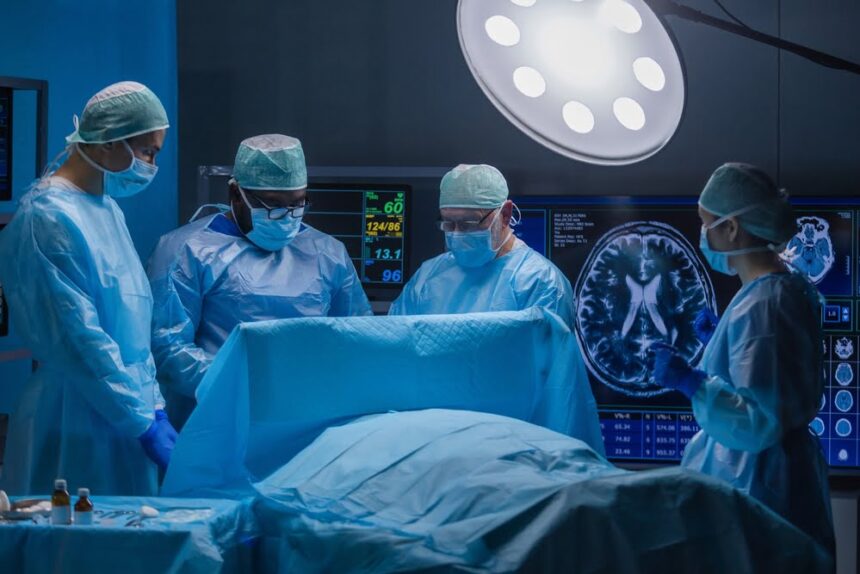
Intraoperative MRI (iMRI)
Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) is a procedure that creates images of the brain during neurosurgery. Most neurosurgeons rely on iMRI to obtain accurate and current images of the brain, guiding them in treating conditions such as epilepsy or removing brain tumors. Using real-time images, neurosurgeons can:
- Locate abnormalities if the brain has shifted. It is common for the brain to shift during surgery, making the pre-surgical imaging less precise. But with the help of iMRI, surgeons can see the most accurate images and information about the brain.
- Differentiate abnormal brain tissue from normal brain tissue. This is particularly important after a traumatic brain injury. Distinguishing the edges of a brain tumor and separating normal tissue from abnormal tissue can be extremely difficult. However, imaging with iMRI during surgery will confirm the successful removal of a brain tumor.
- Protect critical structures. Nowadays, surgeons treat epilepsy using laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT). Through a minimally invasive approach, they heat the tissue and render it inactive by disrupting the flow of seizures. At this stage, neurosurgeons use iMRI to monitor brain temperature to avoid injury during such a procedure.
Neurosurgeons also use robotic stereotactic assistance (ROSA) to treat epilepsy. They place electrodes in the brain using ROSA, which guides them in putting needle-like electrodes into the brain.
Intraoperative Computed Tomography (ICT)
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, intraoperative computed tomography uses advanced medical imaging to increase the safety and accuracy of the placement of electrodes in the brain. Using ICT, neurosurgeons have access to all the information at once, allowing them to make critical decisions during complex and delicate surgeries. Other advantages of ICT include:
- Identifying dangerous areas of bleeding, such as hematoma
- Detecting misplaced screws and preventing unnecessary procedures
- Visualizing changes within the brain as surgery occurs
Stereotactic Computer-Assisted Neurosurgery
The NCBI claims that computer-assisted neurosurgery has become so successful that it is often used in neurosurgical procedures. Stereotactic and computer-assisted techniques have revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of many brain disorders, allowing maximal precision in planning and performing minimally invasive surgical interventions.
Computer-assisted brain surgery treats Parkinson’s disease, brain tumors, epilepsy, and arteriovenous malformations. The neurosurgeon can combine computer-assisted surgery with brain surgery to treat a brain tumor. But in the case of epilepsy, essential tremor, or Parkinson’s disease, computer-assisted surgery may involve deep brain stimulation.
Upcoming Tech in Neuroscience: NeuroTwin or the Digital Twin Brain Technology To Treat Neurological Diseases
Conducted and coordinated by Catalan SME Neuroelectrics Barcelona, Neurotwin is a digital-twin technology for neuroscience that investigates how stimulations of the in silico model can be used to predict and design electromagnetic or pharmacological therapeutic interventions. The project started in January 2021 and will run for 48 months.
Neurotwin involves two research groups: Gustavo Deco and Jordi Garcia Ojalvo. Gustavo Deco’s laboratory focuses on the modeling of the entire brain, attempting to extract and fully understand the mechanisms underlying the global dynamics associated with several brain states.
Garcia-Ojalvo’s laboratory starts by developing a minimal dynamic model of whole-brain activity while identifying the principles that underlie the amplifications of electromagnetics disturbances in brain networks. They currently focus on epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease, but many other disorders or medical conditions can be approached with this technology.
Technology is on the Rise
With so many new upcoming technologies impacting neuroscience, artificial intelligence has dominated in the last few years. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) have become much faster and will likely keep increasing. On the other hand, cybersecurity is also beginning to emerge in neuroscience and radiology, so the privacy of patient records is a significant topic in healthcare in 2022 as well. Many healthcare companies must prioritize their cybersecurity systems to ensure that the tech being used cannot be accessed and manipulated by hackers, which can constitute a problem in the reliability of such technologies.