Last Sunday Dr. Sanjay Gupta interviewed on his show on CNN a pediatrician, Dr. Robert Lustig, who made the assertion that sugar is toxic, and probably carcinogenic. This attention-grabbing statement had earned him a wide following on UTube. But is it true? Let’s examine the evidence.
How is sugar used in the cell?
Last Sunday Dr. Sanjay Gupta interviewed on his show on CNN a pediatrician, Dr. Robert Lustig, who made the assertion that sugar is toxic, and probably carcinogenic. This attention-grabbing statement had earned him a wide following on UTube. But is it true? Let’s examine the evidence.
How is sugar used in the cell?
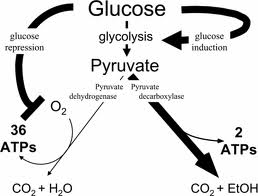
Every cell in our body needs energy in order to survive and perform its functions. Our biochemistry has evolved over billions of years to extract energy from simple sugars, like glucose and fructose. I mentioned the evolutionary ancient-ness (is this a word?) for a reason. In the beginning (Relax, I am not getting into the creation debate) the atmosphere was poor in oxygen. Yet cells had to extract energy from their nutrients. The solution? extract energy from glucose without the participation of oxygen. This process is called anaerobic glycolysis, and even today there are anearobic bacteria that survive solely through glycolysis. This process yields a measly 2 ATP molecules (these are the molecules that store the energy necessary to drive a chemical reaction in the cell), and two 3-carbon molecules of pyruvic acid.
As the ancient atmosphere became enriched with oxygen it became possible to oxidize pyruvic acid, the end product of glycolysis, and extract another 30-36 ATP molecules. At about the same time a species parasitic bacteria invaded the primordial cells, and the two finally settled into a cozy partnership: the cell will provide nutrients and a secure environment to the bacteeria, and the bacteria will provide their capacity to break down pyruvic acid through a chemical process called oxidative phosphorylation using a series of enzymes that make up the electron transport chain, providing the cell with the additional 30 ATP per glucose molecule. And so were born our mitochondria, the tiny powerhouses that inhabit all our cells (except red blood cells).
What does all that have to do with cancer?
Now that we know why the cell needs glucose, and how it obtains the energy it needs out of glucose molecules, we can rationally examine the scary prospect that too much glucose can facilitate cancer.
cancer cells, like any healthy cell, require glucose as their energy source. But if you measured the amount of lactic acid in a solid tumor you’d find a high concentration, and if you measured the pH -it would be lower than in normal tissue. The reason is that cancer cells depend to a large extent on anaerobic glycolysis. And we know that the end-product of that is pyruvic acid, which makes the tumor tissue, well, acidic; hence the low pH. What about lactic acid? It is the product of pyruvic acid when oxidation is not possible. Of course we know it from first -hand experience: when you exercise a muscle to the point that the oxygen supply cannot keep up, you create a lot of lactic acid, which is a pain in the…muscle.
But, you are wondering (I hope), a tumor doesn’t exercise, so why the anaerobic conditions? Enter the evil genius of tumors. When a solitary cell accumulates the proper mutations it becomes a tumor cell, a process called carcinogenesis. The cell divides into daughter cells, those divde again, and so on -until there is a tiny tumor, made of millions of cells. In a sense, a new tissue was created. Except that normal tissue has its own extensive blood supply, but not this tiny tumor: it is made up solely by the tumor cells. So how is a tumor to get its oxygen and nutrients?
The way the tumor cell copes with this dilemma is two-fold. First, it derives it energy from whatever little glucose is available using anaerobic glycloysis and getting 2 ATP molecules per glucose. This state of affairs cannot last forever, because the cell would require enormous amounts of glucose to get enough ATP to fuel its metabolic functions. So the second pillar of the strategy employed by the tumor is to secrete chemicals that stimulate blood vessels in the surrounding normal tissue to sprout new branches that penetrate the tumor and supply it with nutrient and oxygen. This process, called angiogenesis (literally formation of blood vessels) allows the tumor to undergo a new growth spurt, and metastasize to distant organs.
As we said, the initial tumor depends heavily on glycolysis, and because of its inefficiency in extracting energy out of glucose it has a voracious appetite for the sugar. And from that, the “logical” conclusion that sugar is carcinogenic.
Except that it isn’t. Glucose does not cause cancer, or else all living organisms would seccumb to cancer and die. Glucose indeed is utilized by cancer cells to a much larger extent than normal tissue cells. But they get this extra glucose by extracting it a lot more efficiently; they have glucose transporter molecules on their surface (dubbed GLUT) that grab the molecules out of the tissue environment before the normal cells can get to them. So what would one accomplish by depriving himself of glucose? One kills his normal cells before the tumor cells feel the pinch.
Of course, this is a bit oversimplified, but the general idea that glucose does not cause cancer, and deprivation of glucose will not kill the cancer, is valid.
What about the other detrimental effects?
I am in complete agreement that glucose can be harmful. It is associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. It has been shown to damage blood vessels. it is even bad for your teeth. So why take it all? you can get all the glucose you need from complex carbohydrates, and in a much healthier metabolic form.
So try to limit your glucose intake to no more than 15 grams a day (the amount in one can of soda). Get the rest of your energy requirements from grains, fruits and vegetable. And don’t worry about the cancer hype.