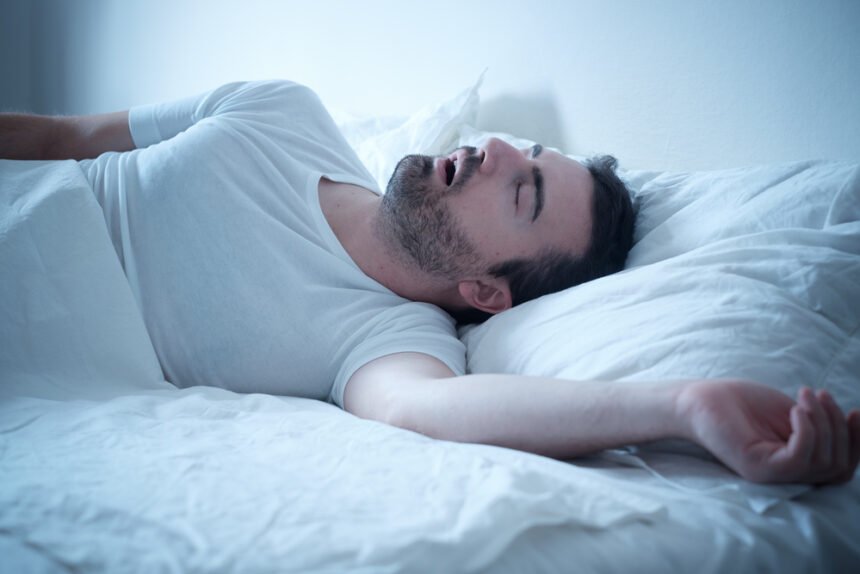
Millions of sleepers across the country suffer from the common problem of snoring. Not only is snoring a possible sign of a more serious issue like sleep apnea, but it can disturb your partner as they try to rest. Most snoring issues can be remedied by simple measures like changing your sleeping position, but in some cases, it may mean there is a more serious problem.
Over 20% of people snore, most of that number is made up of men over 40. That’s a lot of sleepless nights for partners and possible complications from snoring. Although most snorers are not at risk, there are some potential health risks.
Many snorers seek help from experts like Dr. Krueger Sleep & Sinus Clinic, and others try home remedies like wearing nose strips or using ergonomic pillows. If you are regularly snoring, you may want to talk to your doctor about your options. Let’s look at a few health risks of snoring.
Heart Strain
In many cases, snoring is caused by an obstructed airway. When your body has to work harder to bring air into the lungs, it can have a negative effect on your heart and prevent you from getting the rest that you need. An obstructed airway can lead to sleep apnea, which can result in elevated blood pressure. High blood pressure, in turn, causes unnecessary strain on your heart. With increased strain, your heart can become enlarged, which can put you at higher risk for a heart attack or stroke.
Sleep Issues
Snoring or sleep apnea can result in a poor sleep cycle. Interrupted breathing can cause you to wake up frequently during the night, which prevents your body from getting into a deep rest cycle. You may suffer from fatigue due to snoring, putting a strain on your brain and immune system. Chronic sleepiness can affect your ability to concentrate, job performance, and mood.
G.E.R.D.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease is a chronic digestive disorder commonly referred to as acid reflux. People who suffer from GERD experience an uncomfortable back up of stomach acids into the esophagus, causing irritation to the throat’s delicate lining. When you snore or have sleep apnea, your breathing is obstructed by relaxed throat tissues creating a vacuum that pulls stomach fluid back up into your throat. GERD can become chronic and damage your throat and esophagus.
Blood Oxygen
Proper breathing patterns are what regulate the amount of oxygen that is absorbed into your blood. Without the right levels of oxygen in the blood, the delicate vessels in your lungs can become chronically constricted. This type of condition can lead to pulmonary hypertension putting your heart at risk for damage.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregularities in your natural heart rhythms. People who snore often have an uneven pulse and breathing pattern that can result in your heart not working constantly. Arrhythmias on their own are not a huge concern; however, when paired with the other risks associated with snoring, including strain on the heart, there could be a risk for a more serious condition.
If you have been snoring for many years, and you can’t seem to find a solution, or you believe you may have sleep apnea, it’s important to see your doctor. You may be referred to a sleep clinic that will help you find the right solution before your snoring results in a more serious problem.