As someone (most likely French philosopher Blaise Pascal) once said, “I would have written a shorter letter but I didn’t have time.” Stanford Professor Dr.
As someone (most likely French philosopher Blaise Pascal) once said, “I would have written a shorter letter but I didn’t have time.” Stanford Professor Dr. Arnold Milstean started his talk for the Health Innovator’s Collaborative, on “Providing Better Care With Less,” with a variation of this, saying that if he knew his topic better he would only have 4 slides instead of the 8.
Those 8 slides represented so much practical data-driven advice and highly quotable and provocative statements, like “1/3 of healthcare spending could be cut without affecting anything except the quality of life of the providers,” that it’s hard to imagine how rapid fire the content would have been with only 4 slides. Mistean took us along a path to define goals in healthcare transformation and then apply some simple formulas to affecting that change.
To determine some generally agreed upon principles for healthcare improvement, Milstean and team reviewed policy, research reports, and employer and payer surveys. The team found that getting to a 1% annual increase in quality, with a 30% reduction in costs, and a 2.5 percentage point long term increase in spend (less than GDP) would suit most policy recommendations and were therefore to be considered reasonable goals. To bring about this level of change, Milstean recommended implementing an “Old, New, Borrowed, Blue” strategy, which has nothing to do with marriage: it’s just a catchy and easy way to categorize some common sense thinking.
Old: Take a methodical review of existing evidence. As anyone who’s spent much time in healthcare research will tell you, there are a wealth of studies and best practices out there. Given that it takes 17 years to get from research to clinical practice, rather than starting a new study, reviewing what’s been done and implementing best practices is a better way to go.
New: Use technology to automate assessment, help with decision support, and improve workflow. Being at Stanford and working on multi-disciplinary teams lead Milstean to believe that the area healthcare could benefit most from “new” is in healthcare IT. In other industries the move to electronic records produced 2-6 percentage points in productivity improvement after 10 years. Healthcare, with only recent moves to electronic medical records, is just at the beginning of this and hasn’t seen the rewards yet. As well they have just scratched the surface of the digital opportunities.
Borrowed: Look at examples from other countries best practices and figure out how to implement locally. Milstean gave the example of a city in Finland where the time from stroke identification to tPA injection at an ER was 17 minutes. With each minute of time after the onset of stroke representing the death of 1.9 million braincells, emulating the Finnish model can have real impact on quality of patient life and long-term costs. (The average “door to needle” time in the US today is 60-75 minutes.)
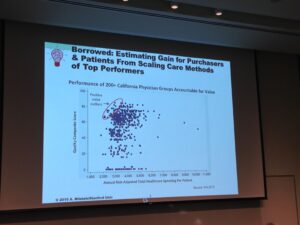
Blue: Focus on human-centered design. Too much of healthcare is not working at the most basic human level, which as it turns out is the place where better and cheaper care resides. Here, Mistean showed a chart of “outliers” physicians who delivered a high-level of care at lower costs than their peers. It turns out what these physicians did differently was at the human level. They truly cared for their patients and looked at the whole patient, not the disease or not the specific incident. These primary care physicians acted as quarterbacks when their patients were managing complex issues with specialists. They cared, caught issues, and also motivated patients to participate in their own care.
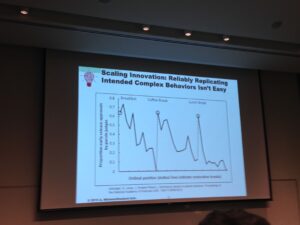
While the formula is simple, it takes a lot of effort to change the system. Some are organization issues like the number of people involved in making any decision. One hospital, trying to implement a new program, took 3 months to get to the kick-off meeting due to the number of people involved in scheduling. The other issue is the human factor in creating repeatable systems.
Here, Milstean used an example from the legal world, where judges were less likely to grant early release when their blood sugar was low. Comparing this to medicine, is remembering that everyone thinks that they are delivering high-quality care, but you often need data to convince them otherwise, and that you need to repeat, repeat, repeat to get to a precision that can cancel out the human factor. As a result, Milstean believes that computer science and behavioral science are two keys to making the big changes we need to improve quality and lower costs in healthcare.