Many public health policy experts believe that Medicare readmissions in the first 30 days after discharge are mostly avoidable and, therefore, indicative of poor quality care. As a result, Medicare has an initiative to reduce readmissions. However, health economist Austin Frakt points to several recent studies that raise doubts about the conventional wisdom. He opines:
Many public health policy experts believe that Medicare readmissions in the first 30 days after discharge are mostly avoidable and, therefore, indicative of poor quality care. As a result, Medicare has an initiative to reduce readmissions. However, health economist Austin Frakt points to several recent studies that raise doubts about the conventional wisdom. He opines:
[I]f we encourage hospitals to reduce readmission rates are we encouraging them to kill people?
The authors of the New England Journal of Medicine article explain:
Our findings suggest that readmissions could be “adversely” affected by a competing risk of death — a patient who dies during the index episode of care can never be readmitted. Hence, if a hospital has a lower mortality rate, then a greater proportion of its discharged patients are eligible for readmission.
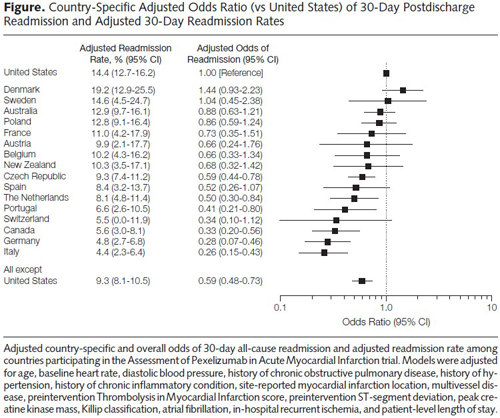
Another study finds the United States rates below almost all OECD countries in readmissions after a heart attack.
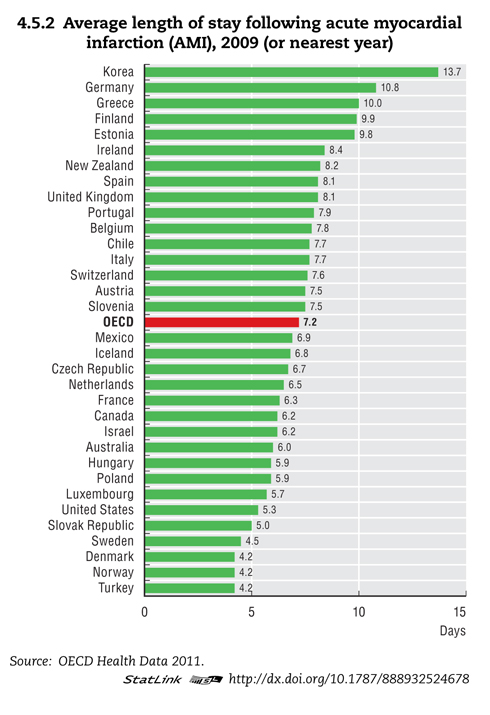 One possible explanation: American hospitals discharge patients sooner than hospitals in OECD countries, as shown in the graph above. Average length of stay (ALS) is a measure of efficiency that U.S. hospitals do well at. A hospital cannot readmit a patient who has never left. Across OECD countries, longer stays are correlated with lower readmissions. Germany has a low readmission rate, an average length of stay double that of the United States.
One possible explanation: American hospitals discharge patients sooner than hospitals in OECD countries, as shown in the graph above. Average length of stay (ALS) is a measure of efficiency that U.S. hospitals do well at. A hospital cannot readmit a patient who has never left. Across OECD countries, longer stays are correlated with lower readmissions. Germany has a low readmission rate, an average length of stay double that of the United States.
Countries with socialized health care systems tend to keep patients in the hospital longer because caring for a heart attack patient convalescing on Day 10 after an attack is far less costly than discharging the patient on Day 5 and admitting a new patient with a serious problem in their place. A convalescing “bed blocker” is a strategy hospitals use to avoid admitting more seriously-ill patients. In the United States, patients are typically discharged sooner to less-expensive facilities. For example, a patient might be discharged from a hospital and transferred to a skilled nursing facility; then later moved to a nursing home; and later discharged to home with home care nursing.
However, one must bear in mind that much of what drives hospital readmission rates are patient-and-community-level elements that are external to the hospital. More so, high readmission may not reflect poor quality, as Frakt is quick to point: high readmission rates can be the result of low mortality rates or good access to hospital care. Indeed, some studies show that improved external care coordination and access to follow-up care actually increases readmissions, hardly indicative of a failure of our health systems.