“These findings are important in part because sleep disturbances can be treated in older people,” Adam Spira, Ph.D., lead author of the study, stated in a press release. “To the degree that poor sleep promotes the development of Alzheimer’s disease, treatments for poor sleep or efforts to maintain healthy sleep patterns may help prevent or slow the progression of Alzheimer disease.” Sponsored by the National Institute on Aging, the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA) began in 1958 when Nathan Shock, Ph.D., chief of Gerontology at the NIH, wondered whether it was possible to study aging by repeatedly evaluating the same people over time. By tracking people as they lived independent lives within their communities, he thought he might be able to better understand what happens as people get older. He also believed that this might help him distinguish between changes due to normal aging and changes due to disease or other causes. Today, more than 1,300 volunteers have made the lifelong commitment to be part of this world-renowned research program. To design the current study, then, Spira and his team of researchers dipped into the coffers of the BLSA. Choosing 70 adults from those currently being tracked by the BLSA, they devised their own neuroimaging sub-study. Chosen participants spanned the ages of 53 to 91 with an average age of 76. First, the researchers asked participants to report on their sleep, including how long they slept and the overall quality of their shut-eye hours. Next, the researchers measured the amount of β-amyloid deposition in their brains, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, via PET (positron emission tomography) scan. Overall, the study participants reported sleep times that ranged from over seven hours to under five and sleep quality from good to poor. After analyzing and comparing the PET scans, the researchers discovered greater Αβ buildup in the brain could be linked to those adults reporting shorter sleep duration and lower sleep quality. “These results could have significant public health implications as Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, and approximately half of older adults have insomnia symptoms,” Spira stated in a press release. He noted that his team’s findings cannot demonstrate a causal link and that other studies are needed to further examine whether poor sleep contributes to or accelerates Alzheimer’s disease. An irreversible, progressive brain disease, Alzheimer’s disease slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and causes problems with behavior. Symptoms usually develop slowly and become worse over time. According to the National Institutes of Health, as many as 5.1 million Americans may have the disease, and currently there is no cure. Researchers do not know what causes the disease, though increasing age is a significant risk factor for developing the illness. The number of people with the disease doubles every five years beyond age 65. Because of this, it is calculated that nearly half of all people aged 85 and older may have Alzheimer’s. Source: Spira AP, Gamaldo AA, An Y, et al. Self-reported Sleep and β-Amyloid Deposition in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. JAMA Neurology. 2013.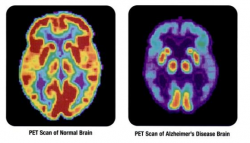 A recent
A recent  A recent study has shown how sleep allows the brain to export cerebral waste— or ‘take out the garbage’ — before it can accumulate and cause dementia and other illnesses. Now, in a paper published online in JAMA Neurology, a team of researchers at Johns Hopkins have discovered that too little sleep or poor quality of sleep is linked to Alzheimer’s disease and may even impact its progression.
A recent study has shown how sleep allows the brain to export cerebral waste— or ‘take out the garbage’ — before it can accumulate and cause dementia and other illnesses. Now, in a paper published online in JAMA Neurology, a team of researchers at Johns Hopkins have discovered that too little sleep or poor quality of sleep is linked to Alzheimer’s disease and may even impact its progression.Tracking Change Over Time
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s Disease Linked to Poor Sleep: Quantity and Quality of Sleep Make a Difference